How connected and autonomous vehicles support a greener future
Posted by | Fuld & Company
The automotive industry is on the cusp of a significant transformation, driven by advancements in connected and autonomous vehicles (CAVs). These technologies are not only poised to revolutionize transportation but also promise substantial environmental benefits.
Route optimization and predictive maintenance
One of the most compelling benefits of CAVs is their potential to optimize routes, thereby reducing energy consumption and emissions. According to a study published in Nature, shared autonomous vehicles significantly reduce energy consumption, facilitating emission reduction and mitigating urban air pollution. Route optimization allows CAVs to navigate the most efficient paths, avoiding traffic congestion and minimizing idle times. This not only saves time for users but also reduces fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
Predictive maintenance is another critical functionality. CAVs equipped with advanced sensors and analytics can predict potential mechanical failures before they occur, ensuring timely maintenance. This prevents breakdowns, reduces downtime, and extends the lifespan of the vehicle, contributing to resource efficiency and sustainability.
Early adopters and growth markets
The adoption of CAV technology varies across regions and market segments. Commercial fleets, particularly in the logistics sector, are among the early adopters. Automated trucks operating in hub-to-hub logistics cycles can drive autonomously on highways, significantly reducing operational costs and addressing the global shortage of truck drivers. This not only enhances efficiency but also reduces emissions, as automated trucks are optimized for fuel efficiency.
Urban public transport is another area witnessing early adoption. Autonomous shuttles and Robotaxis are being trialed in cities worldwide, providing efficient, low-cost, and accessible transportation options. These services can reduce the number of privately owned vehicles on the road, alleviating traffic congestion and reducing overall emissions.
Use cases illustrating environmental benefits
Improved traffic management
In cities, improved traffic management through CAVs can lead to smoother traffic flow and more efficient use of road infrastructure. By receiving real-time traffic information, CAVs can adjust their routes to avoid congestion, reducing travel time and fuel consumption. This also improves road safety by minimizing the risk of accidents.
Public transport integration
Autonomous vehicles can enhance public transport systems by providing flexible, on-demand services. For example, autonomous buses can be summoned to pick up passengers from their homes and transport them to transit hubs, making public transport more convenient and appealing. This can lead to higher public transport usage and lower reliance on personal vehicles.
Truck platooning
This involves groups of trucks driving in close formation, controlled by automated systems. Truck platooning reduces aerodynamic drag, leading to significant fuel savings. It also enhances road safety and optimizes road space usage, contributing to lower emissions and improved traffic efficiency.
Sustainable urban logistics
Autonomous delivery vehicles can streamline urban logistics, reducing the need for multiple delivery trucks and minimizing the environmental impact of last-mile deliveries. These vehicles can operate on electric power, further reducing emissions.
Challenges and future outlook
Despite the promising benefits, the widespread adoption of CAVs faces several challenges, including regulatory hurdles, technological limitations, and public acceptance. Regulatory frameworks need to be updated to accommodate the unique aspects of autonomous driving, such as liability and safety standards. Technologically, achieving full autonomy (Level 5) is still a distant goal, with current developments focused on lower levels of automation.
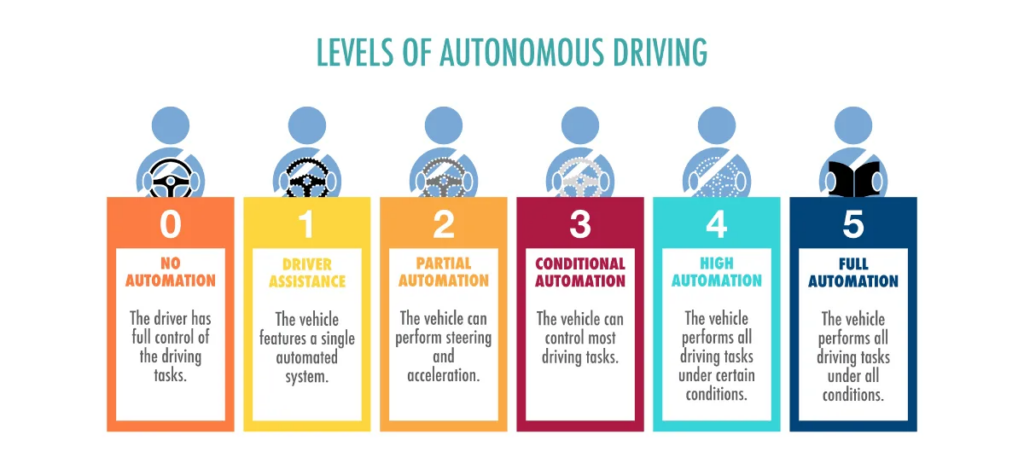
The progress in CAV technology is undeniable. With continuous advancements in AI, machine learning, and sensor technology, the capabilities of autonomous vehicles will only improve. As more early adopters demonstrate the practical benefits and environmental advantages of CAVs, broader market acceptance is likely to follow.
Tags: Automotive, Disruption, Energy, Innovation